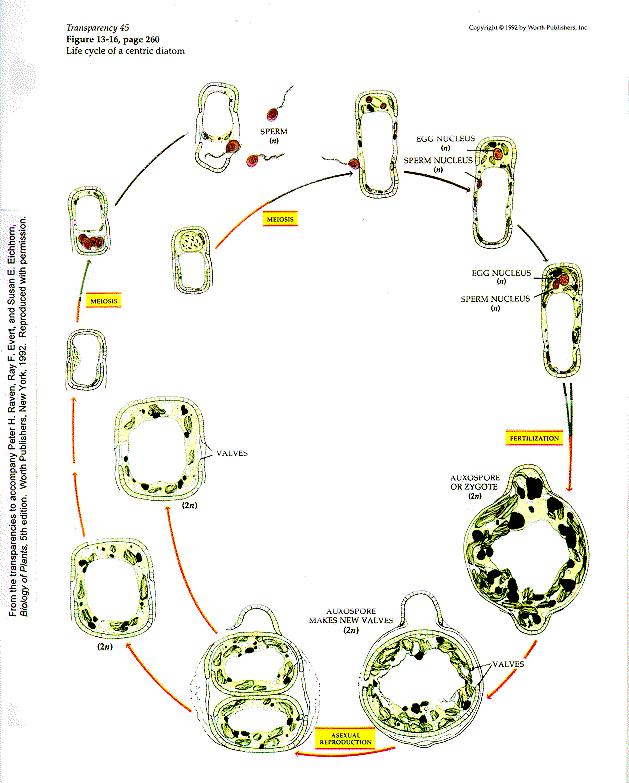
Each daughter cell receives one valve and it is reproduced by furrowing. Diatoms reproduce both asexually and sexually.
Sexually- it is hard to explain look it up on Google.

How diatoms reproduce. It is the most prevalent method of restoring cell size and is often triggered when the size of a cell is less than a critical level usually smaller than half of the original size for most species. In many species sexual reproduction has never been observed and the environmental factors that trigger sexual reproduction in diatoms are not well understood. Some species of Nitzschia a freshwater diatom genus reproduce at a fast rate and may be a cause of some algal blooms.
Sign up and get access to hundreds of high quality instruction. Many diatom species are planktonic suspended in water moving at the mercy of its currents others remain attached to submerged surfaces. These diatoms are capable of producing domoic acid that if ingested can affect the neurological system.
A fast growing marine diatom genus containing species that are toxic is Pseudonitzschia. Most Diatoms use the process of photosynthesis in order to produce their food. Of molecular Biology DIATOMS.
And is used to construct a second smaller frustule the hypotheca. Diatom Reproduction The ability to reproduce sexually is closely associated with cell size. Thus individual diatoms formed from successive bottom halves show a progressive decrease in size with each division.
They are non-motile or capable of only limited movement along a substrate by secretion of mucilaginous material along a slit-like groove or. Diatom - Wikipedia Reproduction among these organisms is primarily asexual by binary fission with each daughter cell receiving one of the parent cells two frustules or theca. Diatoms can reproduce asexually as well as sexually Asexually- shrinking division.
Each daughter cell receives one of the frustules from the parent cell which forms the larger frustule and provides the basis for the construction of the second slightly smaller frustule. Diatoms have a distinctive mode of reproduction called shrinking division which is used in asexual reproduction. Diatoms primarily reproduce asexually via binary fission.
Devaki Course Coordinator Dept. Diatoms normally reproduce by binary fission where one mother cell splits into two daughter cells2. Reproduction among these organisms is asexual by binary fission during which the diatom divides into two parts producing two new diatoms with identical genes.
Most Diatoms do not move much in their lifetime though a type of Diatom called Pennales is known to move in a gliding motion in the water. Diatoms can reproduce in two different ways. Here you will find online education resources curriculum-based for Biology for all classes.
In a few months there can be as much as a 60 percent decrease in average size. CONTENTS Introduction Occurrence Classification Differences and Examples Of Diatoms Cell Structure Reproduction Economic Importance Conclusion References Acknowledgement. Each new organism receives one of the two frustules one larger the other smaller possessed by the parent which is now called the epitheca.
Each daughter cell receives one of the frustules from the parent cell which forms the larger frustule and provides the basis for the construction of the second slightly smaller frustule. Diatoms reproduce asexually by cell division to produce two daugther cells by mitosis. It takes place usually at midnight or in the early morning.
Vegetative reproduction performs with the help of cell division Fig. The cell has vesicles that increase the deposition of silica creating a new valve girdle band. How do Diatoms move.
Diatoms primarily reproduce asexually via binary fission. First of all diatoms can reproduce asexually. This is used by each daughter cell as the larger frustule o.
Inchara R 1st Semester Molecular Biology 30102017 Guided By. Though there are some diatoms that may rely on the nutrients floating in the water for their survival. During reproduction usually by cell division the overlapping shell halves separate and each secretes a usually smaller bottom half.
Diatoms are photosynthesising algae they have a siliceous skeleton frustule and are found in almost every aquatic environment including fresh and marine waters soils in fact almost anywhere moist. Look up what shrinking division is on Google. Under the right conditions diatoms can reproduce very rapidly and a population of a small species can double each day.
Reproducing asexually is the basic method of how diatoms reproduce. Diatom reproduces by vegetative and sexual means.

Diatom Description Characteristics Reproduction Diatom Reproduction Britannica

The Diatom Life Cycle Diatom Life Cycles Meiosis

The Diatom Life Cycle Diatom Life Cycles Meiosis

Untitled Document Microbiology Diatom Marine Biology

Diatoms Reproduce Asexually Through Cell Division When They Cell Divides The New Cell Gets Half Of The Frustule The Other H Diatom Cell Division Life Cycles

They Are One Of The Easiest To Recognize Because Of Their Unique Cell Structure Silicified Cell Wall And Life Cycle Alga

Diatom Single Celled Photosynthesis

This Is The Life Cycle Of A Dinoflagellate Life Cycles Symbiotic Relationships Cell Division

Dinoflagellates Reproduce Through Cellular Division When There Is A Lot Of Nutrients They Can Cause Algal Blooms So Can Diat Diatom Cell Division Life Cycles

Plant Bodies Are Either Bilateral Or Radial In Symmetry Diatom Cell Wall Vegetative Reproduction

Coscinodiscus Light Micrograph Microscopic Diatom Patterns In Nature

Diatom Cell Division Life Cycles

Diatoms Reproduce Asexually Through Cellular Division This Means That It Divides In Half From One Organism To Two Organisms Diatom Life Cycles Algae







Post a Comment